[ad_1]
In a current overview revealed within the journal Vitamins, researchers explored how the dysregulation of intestine microbiota in weight problems impacts adipose tissue (AT) metabolism via direct and oblique results on the mitochondria inside white (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT).
 Research: The Crosstalk between Intestine Microbiota and White Adipose Tissue Mitochondria in Weight problems. Picture Credit score: KateStudio / Shutterstock
Research: The Crosstalk between Intestine Microbiota and White Adipose Tissue Mitochondria in Weight problems. Picture Credit score: KateStudio / Shutterstock
Background
Weight problems, affecting 13% of the worldwide inhabitants as of 2016, has reached epidemic ranges, difficult each developed and growing nations. By 2039, it’s projected that greater than 30% of adults in Europe and much more in the US of America (USA) shall be overweight. This situation arises from a fancy interaction of genetic, life-style, and environmental elements, resulting in extreme power storage in AT. This storage exceeds the tissue’s capability for oxygenation, inflicting irritation, insulin resistance, and elevated cardiometabolic and most cancers dangers. Regardless of intensive examine, the function of mobile and mitochondrial metabolism in weight problems, particularly the affect of intestine microbiota on AT, wants clearer understanding. Figuring out how intestine microbiota impacts AT mitochondria may lay the groundwork for novel weight problems therapies, highlighting the necessity for additional analysis.
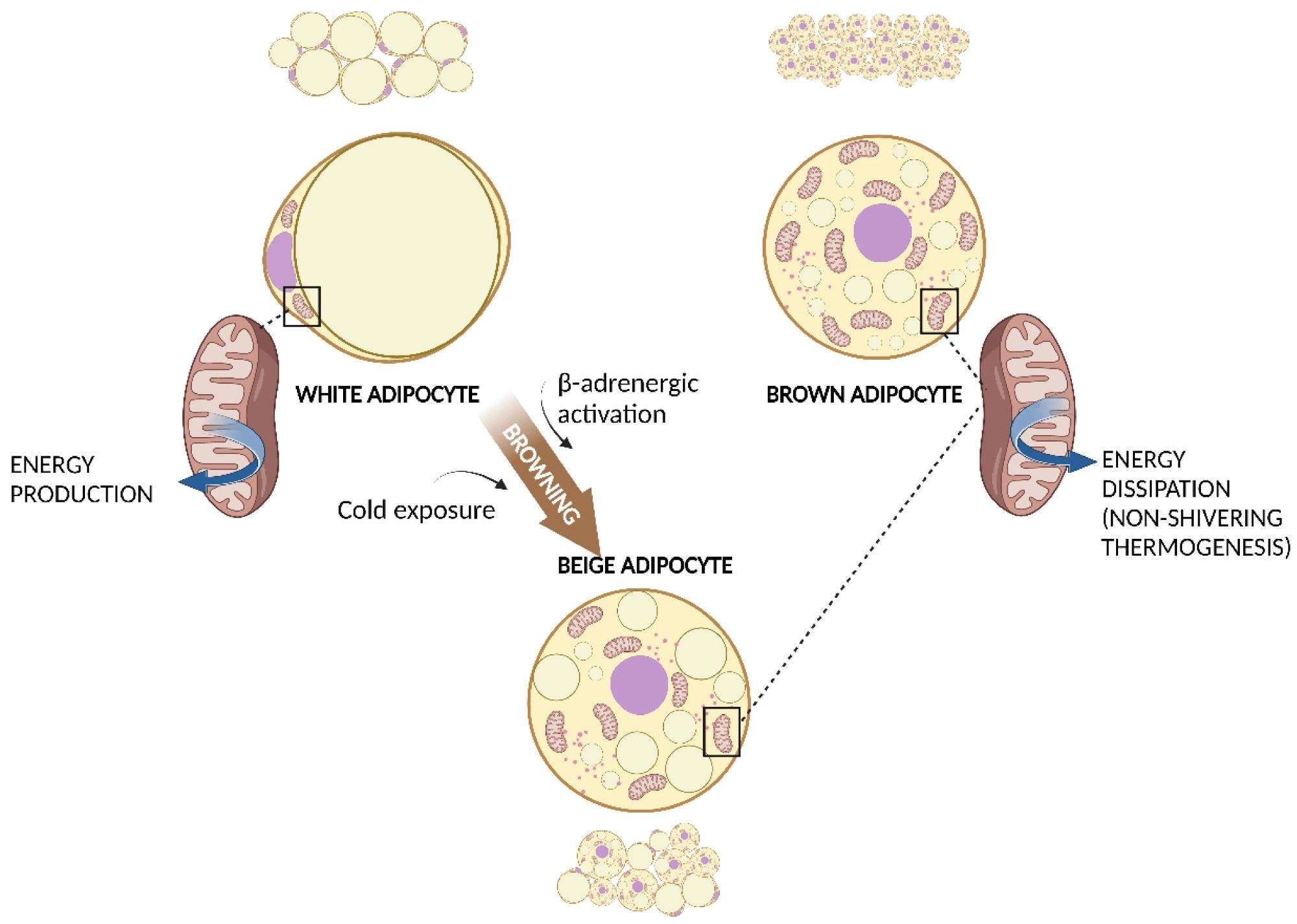 WAT, BAT, and WAT browning. White adipocyte has one giant droplet within the centre of the cell that compresses nucleus and mitochondria at one pole. Brown adipocyte has a number of small lipid droplets and extra mitochondria, unfold out between the droplets. Beige adipocyte has intermediate traits. Chilly publicity and β-adrenergic activation decide the browning of WAT. Each brown and beige mitochondria are concerned in non-shivering thermogenesis. Abbreviations: BAT, brown adipose tissue; WAT, white adipose tissue.
WAT, BAT, and WAT browning. White adipocyte has one giant droplet within the centre of the cell that compresses nucleus and mitochondria at one pole. Brown adipocyte has a number of small lipid droplets and extra mitochondria, unfold out between the droplets. Beige adipocyte has intermediate traits. Chilly publicity and β-adrenergic activation decide the browning of WAT. Each brown and beige mitochondria are concerned in non-shivering thermogenesis. Abbreviations: BAT, brown adipose tissue; WAT, white adipose tissue.
AT: An lively endocrine organ
AT has transcended its conventional view as a mere power reservoir and insulator and is now acknowledged as an lively endocrine organ instrumental in metabolic regulation. This shift is attributed to its secretion of hormones like leptin and adiponectin and quite a lot of cytokines termed adipokines, marking its profound influence on metabolism. Inside this tissue, adipocytes and different cell sorts, corresponding to pre-adipocytes and immune cells, type a fancy mobile surroundings underlying its multifaceted capabilities.
Various capabilities of WAT and BAT
AT, categorised into WAT for power storage and BAT for thermogenic power expenditure, performs very important roles in metabolic well being. WAT’s giant cells retailer fats, contributing to mechanical safety and metabolic regulation, whereas BAT’s smaller, lipid-rich cells generate warmth via non-shivering thermogenesis, providing potential in treating metabolic problems.
The metabolic and endocrine function of AT
Ectopic fats deposition and the activation of ATs spotlight the complexity of their roles in well being and illness. Whereas ectopic fat are related to metabolic problems, the method of “browning” in WAT, whereby cells undertake BAT-like traits, affords therapeutic prospects for metabolic ailments. The endocrine capabilities of WAT additional elucidate its function in power and metabolic homeostasis, with adipokines like leptin and adiponectin enjoying crucial roles. BAT’s contribution to power expenditure via non-shivering thermogenesis represents a basic side of metabolic well being, distinguishing the distinctive contributions of WAT and BAT to the physique’s power steadiness and metabolic regulation.
Mitochondrial operate in AT
Mitochondria play a crucial function in power metabolism inside each WAT and BAT, driving adenosine triphosphate (ATP) manufacturing via nutrient oxidation and regulating lipid metabolism. In WAT, they help lipid synthesis and breakdown, influencing adipocyte differentiation and metabolic well being. Dysfunctional mitochondria in WAT are linked to metabolic ailments because of impaired regulation of adipokines and fatty acid oxidation. Conversely, BAT mitochondria facilitate non-shivering thermogenesis by way of uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1), showcasing their important function in power expenditure. This distinct mitochondrial operate in BAT versus WAT underscores their significance in metabolic regulation and the potential for therapeutic targets in weight problems and associated circumstances.
Mitochondrial dysfunction and weight problems: An in depth connection
Weight problems’s influence on mitochondrial metabolism in AT, notably in WAT and BAT, underscores a crucial side of its pathophysiology. Mitochondrial dysfunction, characterised by altered bioenergetics and impaired lipid and glucose metabolism, performs an vital function in intensifying obesity-related metabolic problems. Research have revealed vital mitochondrial alterations in weight problems, together with diminished expression of mitochondrial proteins, lowered mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid (mtDNA) copy numbers, and decreased exercise of oxidative phosphorylation complexes. These adjustments not solely contribute to inefficient power utilization and storage but in addition foster a shift in the direction of adipocyte hypertrophy, additional selling irritation and insulin resistance. The compromised mitochondrial operate in WAT impacts fatty acid oxidation and adipocyte differentiation, whereas in BAT, it impairs thermogenic effectivity, doubtlessly shifting its metabolism in the direction of a WAT-like phenotype. This connection between mitochondrial dysfunction and weight problems highlights the pressing want for therapeutic methods geared toward restoring mitochondrial well being, providing a promising avenue for weight problems administration and the discount of its related metabolic problems.
The function of intestine microbiota in weight problems and AT mitochondrial operate
The interaction between intestine microbiota and AT mitochondria considerably influences weight problems administration and metabolic well being. The varied intestine ecosystem performs a basic function in metabolic processes, impacting lipid and glucose metabolism via the manufacturing of microbial metabolites like short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). These metabolites have an effect on mitochondrial operate in ATs, modifying fatty acid oxidation and adipocyte differentiation, that are crucial in weight problems development. Dysbiosis, characterised by an imbalance in intestine microbial composition, has been linked to obesity-related metabolic impairments, suggesting that modulating intestine microbiota may supply therapeutic avenues for enhancing mitochondrial operate and combating weight problems. This highlights the need for continued exploration into the intestine microbiota- AT mitochondria axis to develop focused interventions for weight problems and its related metabolic problems.
Journal reference:
- Colangeli L, Escobar Marcillo DI, Simonelli V, Iorio E, Rinaldi T, Sbraccia P, Fortini P, Guglielmi V. The Crosstalk between Intestine Microbiota and White Adipose Tissue Mitochondria in Weight problems. Vitamins. (2023). DOI – 10.3390/nu15071723, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/7/1723
[ad_2]
