A current Vitamins examine compares the composition of the intestine microbiome in prediabetic sufferers and wholesome people.
 Research: Intestine Microbiota in Sufferers with Prediabetes. Picture Credit score: Sebastian Kaulitzki / Shutterstock.com
Research: Intestine Microbiota in Sufferers with Prediabetes. Picture Credit score: Sebastian Kaulitzki / Shutterstock.com
What’s prediabetes?
Prediabetes is outlined as glycated hemoglobin ranges between 5.7-6.5% and fasting blood glucose ranges between 100-126 mg/dL. Prediabetes considerably will increase the mortality dangers and burden on the healthcare system; due to this fact, a number of interventions have been designed to keep up wholesome glucose ranges.
For instance, way of life modifications, bariatric surgical procedure, and medicines are generally used to stop the development of prediabetes to diabetes. Regardless of these interventions, a current American Diabetes Affiliation report indicated that almost all prediabetic sufferers ultimately develop diabetes. Subsequently, it’s crucial to develop more practical interventions to stop or reverse the prediabetic situation.
The intestine microbiome and diabetes
The intestine microbiome performs an important position in regulating lipid and glucose metabolism, as intestine microbial dysbiosis results in the event of many illnesses. For instance, intestinal bacterial composition and abundance modifications affect intestinal permeability, which induces insulin resistance and the introduction of bacterial lipopolysaccharides into the bloodstream.
Intestine microbial dysbiosis is straight related to elevated intestine permeability, which promotes low-grade systemic irritation. This situation is a key contributor to metabolic syndrome and varied persistent illnesses, equivalent to sort 2 diabetes.
Contemplating these observations, it is very important perceive the mechanism by which intestinal micro organism alterations affect the growth of diabetes. This data may finally assist the event of novel approaches to stop the development of prediabetes to diabetes.
Food regimen, medicine, and age play an necessary position in altering the intestine microbiota. Though a number of research have established differential intestinal micro organism between diabetic and wholesome people, few research have assessed intestinal micro organism composition in prediabetic sufferers and its impression on the physiological mechanisms of this well being situation.
Concerning the examine
The present examine in contrast intestine microbial composition between prediabetic sufferers and wholesome people. The impression of food plan on the intestine microbiome of prediabetic sufferers was additionally assessed in an effort to establish nutrition-based interventions that might probably stop the development of prediabetes to diabetes.
A complete of 57 examine contributors had been recruited from Taipei Tzu-Chi Hospital in Taiwan. Intestine microbiota information of 60 wholesome people between 18 and 65 years had been obtained from biobanks and used because the reference group.
Research contributors had been suggested to maintain a three-day meals file and acquire fecal samples on the third day. The nutrient composition of the contributors’ food plan was measured utilizing Nutritionist Skilled software program 2.0.
Research findings
The composition, variety, and abundance of the intestine microbiota had been considerably lowered in prediabetic sufferers in comparison with wholesome people. This discovering was according to earlier research that indicated differential microbial composition in sufferers with diabetes. Prediabetic sufferers additionally exhibited a better physique mass index (BMI) than controls.
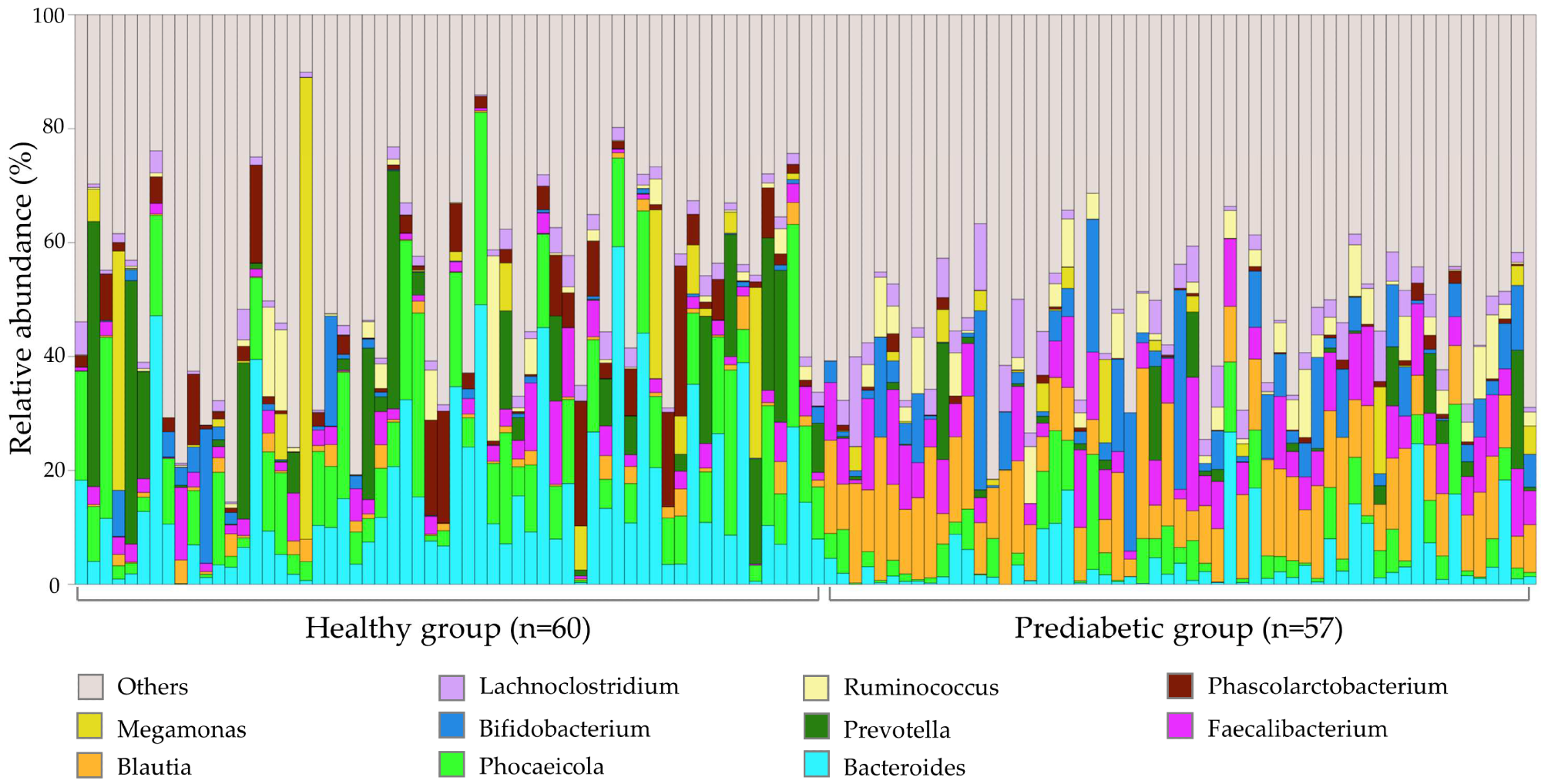 Intestine microbiome profile of 117 fecal samples on the genus stage. The remaining bacterial genera are summed as ‘Others’.
Intestine microbiome profile of 117 fecal samples on the genus stage. The remaining bacterial genera are summed as ‘Others’.
According to earlier research on sort 2 diabetes, the present examine reported greater ranges of Mediterraneibacter, Bifidobacterium, Blautia, Anaerostipes, Clostridium, and Butyricicoccus within the fecal samples of wholesome people than prediabetic sufferers.
Earlier research have proven that butyrate maintains the integrity of the intestinal mucosa. This metabolite is synthesized by intestine micro organism, specifically, Anaerostipes and Faecalibacterium.
Sustaining the integrity of intestinal mucosa can stop the invasion of pathogenic micro organism within the blood and the destruction of pancreatic β-cells. This discovering signifies the oblique position of Anaerostipes and Faecalibacterium in regulating blood glucose ranges.
In distinction to prediabetic samples, wholesome fecal samples exhibited excessive ranges of Eggerthella and Streptococcus. Nevertheless, a better abundance of Phascolarctobacterium, Bacteroides, Paraprevotella, and Parabacteroides was noticed in prediabetic fecal samples.
Prediabetic sufferers exhibited a number of altered physiological metabolic pathways, which have an effect on insulin transmembrane signaling and overexpression of retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I). This metabolic dysfunction triggers immune cells to assault β cells, affecting blood glucose ranges. Earlier research have additionally indicated that irregular sphingolipid metabolism results in insulin resistance and neuronal apoptosis.
Food regimen performs an important position in sustaining intestine bacterial variety and abundance. Subsequently, prediabetic sufferers are suggested to devour a low carbohydrate (LC) food plan with a better dietary fiber consumption. This mix may enhance intestinal barrier integrity, thereby stopping the development of prediabetes to diabetes.
Conclusions
Differential intestine microbial composition and abundance had been noticed in prediabetic sufferers in comparison with wholesome controls. This distinction can be related to altered metabolic and physiological responses. These findings recommend that bettering the intestine microbiome may stop the onset of diabetes by sustaining regular physiological metabolism.
Journal reference:
- Chang, W., Chen, Y., Tseng, H., et al. (2024). Intestine Microbiota in Sufferers with Prediabetes. Vitamins 16(8); 1105. doi:10.3390/nu16081105
